CITC Ltd News
Follow us on to be updated on what’s going on in-&-out CITC Ltd in relation to business, science, awards, grants, collaborations, job opportunities, and anything that is worth knowing about us.
Press Release - King’s College London and CITC join forces to help bring the next generation of stem cells into the clinicCambridge, 1st November 2019 - Cambridge Innovation Technologies Consulting (CITC) Ltd. and King’s College London have entered into an exciting research project as part of the Collaborate to Innovate programme.
The project will bring together the expertise of Professor Francesco Dazzi’s research group in growing and manufacturing mesenchymal stem cells, with the experience of CITC Ltd. in induced neural stem cell (iNSC) technology.
Part of London Advanced Therapies and funded by Research England, this round of the Collaborate to Innovate programme provides funding and support to collaborative projects between SMEs and academic research groups working in the field of advanced therapies. Collaborate to Innovate is managed centrally by MedCity, the life sciences cluster organization for London and the greater south-east.

The project will apply the knowledge of the King’s College London research team in Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) to develop and perform quality control assessments of human iNSCs with the ultimate goal of scaling-up the process to help develop therapies for patients affected by progressive forms of Multiple Sclerosis. iNSCs, generated by direct reprogramming of a patient’s skin or blood cells, recapitulate the exciting therapeutic characteristics of other neural stem cell sources but with fewer practical, ethical, and safety concerns.
The collaboration aims to create a Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) by which human iNSCs are expanded and assessed accordingly to ensure they meet the requirements set out by the GMP standards.
Commenting on the partnership, Stefano Pluchino, Co-founder and CSO of CITC said, ‘CITC Ltd is extremely excited to partner with Professor Francesco Dazzi at King’s College of London on this highly strategic project which holds huge potential to expedite the translation of next-generation brain stem cell therapies into the clinic’.
Francesco Dazzi, Professor of Regenerative & Haematological Medicine at King’s College London, said, ‘We are absolutely delighted to be given the opportunity to pave the way for a truly innovative and game-changing approach that may improve the lives of patients affected by progressive forms of multiple sclerosis. Our facility has already made it possible to manufacture mesenchymal stem cells, hepatocytes and lentiviral vectors, all of which are in clinical practice. The collaboration with CITC Ltd. is a new challenge and we are thrilled that we will be working together. We at King’s College London are confident that, with their scientific knowledge and our experience in GMP practice, we will forge a successful venture.’
   
Read More
Press Release - CITC’S approach to Exogenous Stem Cell Therapies aligns with Google’s Healthcare and Medicines policy against unproven therapies Cambridge, 12th September 2019 - Google has just announced a new Healthcare and Medicines policy that prohibits advertising for unproven or experimental medical techniques such as most stem cell therapy, cellular (non-stem) therapy, and gene therapy.

Commenting on the matter, Stefano Pluchino, University Reader in Regenerative Neuroimmunology a Cambridge University and CSO at CITC Ltd says ‘ This new policy is extremely timing, as formal action is required to contrast the widespread marketing of unscrupulous medical products such as unproven stem cell therapies. Important medical discoveries often start as unproven ideas. However, monitored and regulated clinical trials are the only reliable way to test and prove important medical advances that include those represented by molecular medicines such as cellular and non cellular therapies and gene therapies. ’
Commenting further on the matter, Luigi Occhipinti, CEO and Director of Engineering at CITC Ltd adds “ Our iStem4Life(R) project aims to spin-out a wholly dedicated initiative undertaking late pre-clinical in vitro and in vivo work in preparation for a first-in-human clinical trial with induced Neural Stem Cell transplants for patients with progressive forms of Multiple Sclerosis in the UK. Seeking approval by the Medicinal and Healthcare Regulatory Agency (MHRA) is therefore the next step towards this important milestone. ”
CITC Ltd. is in complete alignment with the statements provided by theInternational Society for Stem Cell Research (ISSCR), in which this new Google’s policy is very welcomed. CITC Ltd trust this will be a good step towards less undertaking of unproven therapies.
Read More
News
- CITC Ltd appoints Research Laboratory Technician
Cambridge, 17th June 2019 - CITC is delighted to welcome Lorenzo Mazza on board as Research Laboratory Technician to join the Innovate UK funded 'Humanase' feasibility study entailing the characterisation of a novel human-derived chemotherapeutic enzyme and a formulated drug based on it.
A powerful therapeutic strategy against some cancers, notably Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia (ALL), has been to starve the cells of ASN by utilizing the enzyme L-asparaginase (ASNase), currently bacterially derived. 'Humanase' aims to investigate a potential remedy to the shortcomings of ASNase by characterising the efficacy and therapeutic potential of an alternative
human Asparaginase-like protein 1 (hASRGL1)
Read More
Press Release
– In the latest issue of Cell CITC Ltd preview a significant new paper by Jeppesen et al. reassessing the composition of extracellular vesicles
Cambridge, 11
th
April 2019 – CITC’s own Stefano Pluchino and Jayden Smith have published in Cell an invited article
Explicating Exosomes: Reclassifying the Rising Stars of Intercellular Communication
, in which they preview an important new paper from Robert J. Coffey’s lab at Vanderbilt University that re-examines the biomolecular composition of exosomes.
Exosomes are a particular species of extracellular vesicle (EV), small membranous particles released by cells that play important roles in physiological function and disease as agents of intercellular communication. As such, EVs are being explored as potential biomarkers by which to diagnose or prognosticate conditions such as cancer or neurological disorders. Conversely, there is significant interest in repurposing or re-engineering EVs as potential drug-delivery vehicles, an approach we are exploring through our
humaNase
project with respect to EV-based delivery of human Asparaginase-like protein 1, a potential chemotherapeutic.
In the latest issue of
Cell
Coffey’s team have provided a stringent re-characterisation of the accepted markers and molecular cargo of exosomes (
Reassessment of Exosome Composition
by Jeppesen et al.), challenging several of the accepted properties of these EVs. Notably, their work demonstrates that DNA is not actively released from cells via exosomes or other small EVs; they instead propose a novel, parallel secretion mechanism. Our accompanying preview article provides a context for Jeppesen et al.’s findings, reflecting on the need for further elucidation of the mechanisms through which EVs arise and a precise characterisation of heterogeneous EV species in the attribution of biological function.
Both papers have been featured among 18 selected Cell articles describing the latest progress in unraveling the secrets of exRNA, within the
Insights from the Extracellular RNA Communication Consortium
recource.
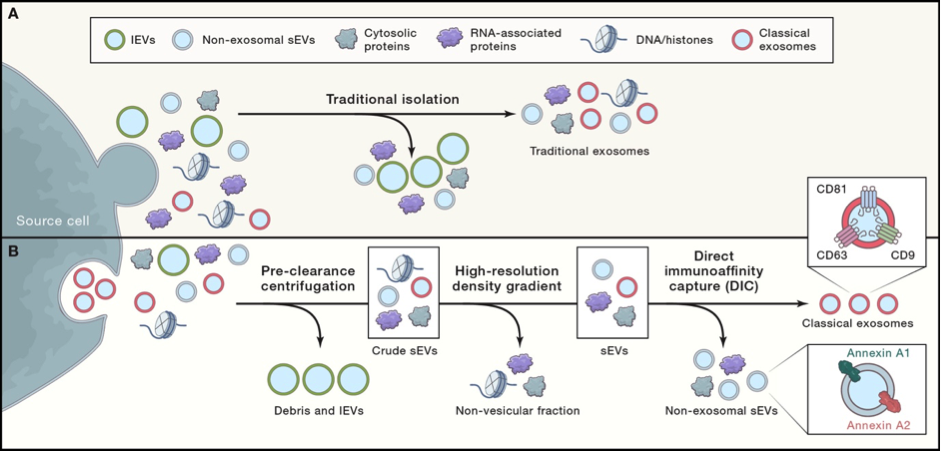
Figure 1. Traditional versus revised exosome isolation protocols.
From S Pluchino & JA Smith, Explicating Exosomes: Reclassifying the Rising Stars of Intercellular Communication,
Cell
2019;
177
: 225-227; and DK Jeppesen et al., Reassessment of Exosome Composition,
Cell
2019;
177
: 428-445.
About CITC Ltd:
CITC Ltd (Cambridge Innovation Technologies Consulting Ltd) is a technology consulting and medical research company based in Cambridge (UK) with the mission to provide innovation in high tech fields that require multi-disciplinary approaches and know-how, from bio-electronics, integrated smart sensors and systems, to advanced medical solutions.
Read More
News
-
CITC shares its experience following 18 months of participation in the CUPIDO project targeting new treatments for Cardiovascular Diseases
Cambridge 13th March 2019 - The EU-funded project, CUPIDO, which started in February 2017, proposes the application of nanotechnologies to target cardiovascular disease. Exploiting such a tiny system as a route of administration can revolutionise the cardiovascular field, becoming the first non-invasive and heart-specific therapy. To achieve the goal, the CUPIDO consortium is working to develop biocompatible and biodegradable nanoparticles that can self-assemble and encapsulate drugs (novel or available) for cardiovascular disease.
CITC, being an active member of this consortium is mainly involved in the coordination of the project exploitation and supporting the regulatory pathways, to help bring the results from lab to market. Learn more about the innovation of CUPIDO as well as CITCs role in the video interview of our Head of Marketing and Communication.
Video Interview
Press Release
-
"RESTORE
Health by Advanced Therapies" to become billion-euro 'flagship'
Cambridge, 4th March 2019 - We are delighted to announce that the consortium "
RESTORE
Health by Advanced
Therapies”
has been selected to compete to become one of the European Commission’s next billion-euro ‘flagship’ science initiatives.
The Commission chose the 6 candidates in December from a list of 16 proposals. Out of the six submitted stage-2 proposals in the category of “Health and Life Sciences”, LifeTime (single cell analysis) and
RESTORE
(Advanced Therapies) were selected for the final run.
The Large Scale Research Initiative
RESTORE
will be a “place” where medicine, basic research, technology development and engineering meet, communicate and work together: to tackle grand interdisciplinary science and technology challenges and to find novel solutions.
RESTORE
aims to build a coordinated, financially strong, academia-industry partnership to result in game-changing impact on Europe´s economy and society. The unifying goal of
RESTORE
is the implementation of newly developed Advanced Therapies in clinical routine to improve patients´ outcome with high impact on Europe´s society and economy.
Starting in Spring 2019,
RESTORE
will receive €1 million (US$1.1 million) to develop a detailed feasibility proposal over the next year. Up to three (of the initially shortlisted) consortia will be chosen to become full initiatives to launch in 2021.
RESTORE
will be structured in five Research and Innovation Action (RIA) modules to address these major challenges:
-
·
Basic Science and Early Development
-
·
Manufacturing of Advanced Therapy Medicinal Products and Biologised Medical Devices, including product characterization
-
·
Advanced Preclinical Models
-
·
Biomarkers for in-depth analysis of patients´ response to Advanced Therapies
-
·
Clinical Research and Implementation
CITC Ltd and our collaborators at the University of Cambridge are proudly represented amongst the stakeholders who have committed to support RESTORE.
www.restore-h2020.eu
Read More
Press Release -
CITC Ltd awarded with an Innovate UK Health and Life Sciences competition grant to investigate the potential of novel chemotherapies in its
humaNase
project
Cambridge, 2nd August 2018 - Innovate UK, the UK’s innovation agency has awarded CITC Ltd funding for their
humaNase
project.
Cancerous cells are notorious for undergoing metabolic changes and require amino acids such as L-asparagine (ASN) to grow. A powerful therapeutic strategy against some cancers, notably Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia (ALL), has been to starve the cells of ASN by utilizing the enzyme L-asparaginase (ASNase) which converts ASN to aspartate which cannot be used by cancerous cells. The ASNase enzymes currently employed clinically are derived from bacteria, meaning they frequently invoke allergic reactions in patients, and they can give rise to toxic side effects due to unwanted glutaminase (GLS) activity of the ASNase.
Through
humaNase
, CITC Ltd aims to investigate a potential remedy to these shortcomings by characterising the efficacy and therapeutic potential of the ASNase alternative
human Asparaginase-like protein 1 (hASRGL1)
. The recent discovery of a human-compatible hASRGL1 trafficked by vesicles secreted by neural stem cells and free of GLS activity (Iraci, Gaude et al. Nat Chem Biol, 2017) provides the pivotal IP leading to
humaNase
(c.f.r. see previous Press Release 3
rd
July 2017).
Commenting on the project,
Luigi Occhipinti, CEO, Founder and Director of Engineering at CITC Ltd
says
“we are thrilled to start this industrial feasibility project which allow us to build upon the discovery of human Asparaginase Like 1 protein by leading scientists at Cambridge University, and to investigate the therapeutic potential of this enzyme toward more sustainable and minimally invasive cancer therapies, ideally suited for treatment of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia, and other malignancies”.
Jayden Smith, the humaNase Project Manager at CITC Ltd,
had this to say:
“While asparaginases are ubiquitous in the treatment of ALL, issues arising from their bacterial origin and off-target side-reactions cause significant tolerability issues, necessitating complicated scheduling and dosage regimes and swapping to asparaginases from different bacterial species. These complications are especially evident in adult patients, for whom ALL has an especially poor prognosis. humaNase aims to provide a thorough fundamental characterization of an ostensibly fully-tolerable, non-toxic alternative to the currently-used asparaginases, with an eye towards developing hASRGL1 into a safer ALL therapy.”
About CITC Ltd:
CITC Ltd (Cambridge Innovation Technologies Consulting Ltd) is a technology consulting and medical research company based in Cambridge (UK) with the mission to provide innovation in high tech fields that require multi-disciplinary approaches and know-how: from bio-electronics, integrated smart sensors and systems to advanced medical solutions.
Read More
Press Release
- CITC partners in the new B2B European consortium to develop the first 3D organ-on-chip device modelling Breast Cancer
Cambridge, 30th July 2018 - The European project B2B aims at Modelling spontaneous
B
reast cancer metastasis
to
the
B
one with a first-of-its-kind 3D device that recapitulates physiological tissue-level complexity.
1 in 8 woman are affected by Breast Cancer, and it’s most common metastatic site is the bone. The mechanism by which these breast cancer cells spread to the bone is still largely unknown, this lack of understanding is a major stumbling block to overcoming breast cancer mortaility. Up to date there have been no metastasis-supressing agents found.
The aim of the device would be to dissect the complexity of the metastatic process and empower high-throughput drug screening in a physiological context in order to gain a better understanding of this mechanism and potentially lead to the identification of metastasis-supressing therapies.
CITC’s Senior Research Associate,
Dr Jayden Smith
, and
Miss Nicole Harrington
, Head of Communications and Marketing at CITC Ltd, participated in the project’s kick-off meeting earlier this month, in Genova, Italy, at the CNR, IEIIT premises.
Commenting on the project,
Luigi Occhipinti, CEO, Founder and Director of Engineering at CITC Ltd
says
“we are delighted to be part of this unique consortium coordinated by the CNR in Italy and participated by leading research organizations and companies in Switzerland, Netherlands, Italy, Greece and the UK. B2B aims at developing a modern approach to screen the effect of emerging metastasis-suppressing therapies in Breast Cancer
.
The targeted device will be a world-first 3D organ-on-chip able to reproduce the pathological process responsible of bone metastasis, with unprecedented tissue-level complexity and accuracy achievable in the lab”
About CITC Ltd (
www.citc-ltd.com
):
CITC Ltd (Cambridge Innovation Technologies Consulting Ltd) is a technology consulting and medical research company based in Cambridge (UK) with the mission to provide innovation in high tech fields that require multi-disciplinary approaches and know-how: from bio-electronics, integrated smart sensors and systems to advanced medical solutions.
About B2B:
B2B is a new Research and Innovation Action collaborative project funded by the European Union under the Horizon 2020 programme for Future and Emerging Technologies (call H2020-EU.1.2.1. - FET Open, Project No. 801159), coordinated by the National Research Council (CNR, Italy), IEIIT institute, and participated by the University of Basel (Switzerland), Department of Biomedicine, Universiteit Maastricht (NL), React4Life Srl (Italy), IN Srl (Italy), Erasmus Universitair Medish Centrum Rotterdam (NL), Texnologikes Lyseis Bioekpompis IKE (BET solutions, Greece) and Cambridge Innovation Technologies Consulting (CITC) Ltd (UK).
Read More
Press Release
- CITC Ltd partner with Zinergy at IDTechEx conference to introduce its new Patch4Life™ platform to the public for the first time
.
12
th
April 2018 – Berlin, Germany
- The IDTechEx Conference (
emerging technologies unleashed
) in Berlin yesterday, saw CEO of Zinergy, Dr Pritesh Hiralal discuss the future of printed, flexible energy storage and its application in healthcare patches with specific reference to CITC’s Patch4life™ and the technology used within
Over the last 9 months CITC Ltd and Zinergy have been developing the world’s lightest and smartest
“Wear-and-Forget”
Companion Device for Ambient Assisted Living. This thin, comfortable and lightweight patch is designed for use in both hospitals and at home for 24/7 personalised health and environmental monitoring.
Packaged in a waterproof, flexible and stretchable wristband or adhesive patch, the new Patch4life™ comes with a full set of sensors for smart analysis of motion patterns, body and environmental data along with Zinergy’s ultra-thin film battery and supercapacitor technology, and a state-of-the-art wireless energy harvester and power management, for 24/7 autonomous continuous operation.
Read More
Press Release
–
Personalised stem cell treatment to provide relief to people with progressive MS
Cambridge, 22
nd
February 2017
- Scientists within the Department of Clinical Neurosciences at Cambridge University with close links with CITC Ltd. have demonstrated the ability to directly re-programme skin cells into brain stem cells that when transplanted into the central nervous system help reduce inflammation and may help repair the damaged tissue caused by multiple sclerosis.
This study - performed in mice and published online today in the journal
Cell Stem Cell
– is a major step towards the development of personalised stem cell treatment based on using a patient’s own skin cells to treat chronic illnesses of the CNS.
Advances in stem cell biology have raised great expectations that diseases of the central nervous system (CNS) may be improved by the development of stem cell therapies. Previous work from the Cambridge team showed that transplanting brain stem cells (NSCs) reduces inflammation and improves the pathological features of multiple sclerosis (MS)-like disease in laboratory animals. A limitation to this therapy though, was the origin of the stem cells, their stability as well as immunological factors.
A possible solution to this would be to use skin cells that are converted into brain stem cells (iNSCs). These iNSCs are generated by directly re-programming adult fibroblasts into NSCs. As these iNSCs would be patient specific an adverse immune response would be avoided. Adding to this, the generation of these cells occurs rapidly, within three – four weeks.
In MS, the body’s immune system attacks and damages the myelin sheath that surrounds nerve fibres resulting in a disruption of the essential messages sent to and from the CNS. This deterioration leads to neurological symptoms such as a decrease in motor function, and in turn can lead to greater forms of disability.
With progressive forms of MS chronic inflammation is sustained by a widespread activation of cells known as microglia and macrophages, which under normal conditions are involved in extracting foreign particles, whereas in diseased conditions they attack the CNS causing the aforementioned chronic inflammation.
Chronic MS, in turn leads to a significant increase in the metabolite succinate, a key inflammatory signal as it induces the transcription of interleukin (IL)-1 (a protein that stimulates immune responses including inflammation) both intracellularly as well as extracellularly. Transplanting iNSCs directly into the cerebrospinal fluid reduces the amount of succinate freely available due their ability to take up this metabolite, which then causes a cascade towards an anti-inflammatory effect and subsequently a decrease in the secondary damaged caused to the CNS.
Commenting on the study,
Dr. Stefano Pluchino
,
University Reader in Regenerative Neuroimmunology at Cambridge University and CSO at CITC Ltd
. says “Our mouse study suggests that using a patient’s reprogrammed cells could provide a route to personalised treatment of chronic inflammatory diseases, including progressive forms of MS. This is particularly promising as these cells should be more readily obtainable than conventional neural stem cells and would not carry the risk of an adverse immune response.”
Dr. Luca Peruzzotti-Jametti
, the first author on this study and a
Wellcome Trust Research Training Fellow and Consultant at CITC Ltd
. says “We made this discovery by bringing together researchers from diverse fields including regenerative medicine, cancer, mitochondrial biology, inflammation and stroke and cellular reprogramming. Without this multidisciplinary collaboration, many of these insights would not have been possible."
This research was funded by the European Research Council, Medical Research Council, the Italian Multiple Sclerosis Association, the Congressionally-Directed Medical Research Programs (CDMRP), the Evelyn Trust and the Bascule Charitable Trust.
Reference
Peruzzotti-Jametti L. Bernstock J.D., Vicario N., Costa Ana S.H., Kwok C.K., Leonardi T., Booty L.M., Bicci I., Balzarotti B., Volpe G., Mallucci G., Manferrari G., Donegà M., Iraci N., Braga A., Hallenbeck J.M., Murphy M.P., Edenhofer F., Frezza C., Pluchino S.
Macrophage-derived extracellular succinate licenses neural stem cells to suppress chronic neuroinflammation.
Cell Stem Cell
2018; 22: 1-14.
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2018.01.20
Read More
Press release
- RNA nanotherapeutics to inhibit neurotoxic glial responses
Cambridge, 10th December 2017
- Research conducted by CITC Ltd scientists in conjunction with the Department of Clinical Neurosciences and Stem Cell Institute at Cambridge University demonstrates that RNA nanotherapeutics curtail the production of an inflammation-spreading signal released by cells of the central nervous system (CNS) in response to injury or disease.
Astrocytes are a ubiquitous and functionally-diverse class of cells found in the CNS where they play essential roles in regulating physiological processes such as synaptic transmission and blood-brain barrier integrity. Insults to the CNS, including conditions as diverse as traumatic injuries of the brain and spinal cord, multiple sclerosis, brain stroke and Alzheimer’s disease, are known to invoke a reactive state in astrocytes during which these cells undergo a variety of morphological and functional changes. Astroglial changes can be beneficial or detrimental, depending on the type, timing and context of the insult. Reactive astroglial cells typically increase the expression and release of the inflammation- and reactivity-propagating protein Lipocalin 2 (Lcn2). Lcn2 secreted by reactive astrocytes is known to promote reactivity in otherwise resting astrocytes, polarise immune cells towards a pro-inflammatory state, and have toxic effects on neurons.
Using the bio-inspired three-way junction (3WJ) RNA nanotechnology originally developed in the lab of Dr. Peixuan Guo at Ohio State University (USA), this research conducted by Jayden A. Smith demonstrated that RNA interference can efficaciously and safely down-regulate the expression of Lcn2 in reactive astrocytes
in vitro
. Moreover, treatment with anti-
Lcn2
-3WJs significantly impeded the ability of reactive astrocytes to perpetuate a pro-inflammatory state. Resting astrocytes receiving the culture media in which reactive astrocytes had been grown showed a large increase in the expression of Lcn2 and nitric oxide synthase 2 (Nos2), an enzyme that produces free radicals and is associated with inflammation. Treating the original reactive astrocytes with anti-
Lcn2
-3WJs negated this effect. Importantly, 3WJ-mediated Lcn2 reduction was also evident in an experimental mouse model of contusion spinal cord injury, with significant reductions in the amount of Lcn2 present in mice treated with the RNA nanotherapeutics.
“
This proof-of-concept study has important implications for the treatment of brain disorders in which inflammation is often a contributing factor in the pathology
,” explains Smith, now Senior Research Associate (SRA) at CITC Ltd. “
The approach is especially well-suited to combinatorial treatments in which the inhospitable tissue microenvironment fostered by the local increase in Lcn2 might prove inhibitory to other putative regenerative interventions, such as small molecules or stem cell therapeutics. Moreover, the modular, multiarmed nature of the 3WJ nanostructure lends itself to further functionalisation, with the potential for engineering targeting and/or diagnostic capabilities into the platform for the development of cell-specific therapeutics.
”
This research was funded by the International Foundation for Research in Paraplegia, the Bascule Charitable Trust, the UK Regenerative Medicine Platform, and Wings for Life.
Full article in: Molecular Therapy – Nucleic Acids
Publication details
Jayden A. Smith, Alice Braga, Jeroen Verheyen, Silvia Basilico, Sara Bandiera, Clara Alfaro-Cervello, Luca Peruzzotti-Jametti, Dan Shu, Farzin Haque, Peixuan Guo, and Stefano Pluchino.
RNA nanotherapeutics for the amelioration of astroglial
reactivity. (http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2162253117302925)
Read More
News
- CITC Ltd. appoints a Research Associate and Project Manager
Cambridge, 1
st
November 2017
- CITC Ltd has appointed Dr. Jayden Aaron Smith as a Senior Research Associate and Project Manager. Dr. Smith, an expertly trained Chemist and Computer scientist, as well as pRNA nanotechnologist, has begun his involvement in the CUPIDO project, which aims at developing Cardio Ultrefficient nanoParticles for Inhalation of Drug prOducts.
I
am very excited to join this new venture and eager to challenge myself in this new role
– J.A. Smith, SRA, CITC Ltd
I am fully confident Jayden will succeed in business as much as he has done in academic research
– S. Pluchino, Cambridge University Reader in Regenerative Neuroimmunology and CSO, CITC Ltd.
CITC Ltd has resident research staff located within the Clinical School – Dept of Clinical Neurosciences at Cambridge University, which will allow the exploitation of new synergies in the field of drug discovery and nano therapeutics.
Read More
News
- EC-funded project on nanoparticle-assisted drug delivery in cardiology (CUPIDO; GA No 720834)


Bologna, October 2017
- The incidence of Cardiovascular Disease (CD) claims worldwide 17.1 million lives a year, with an estimated 31% of all deaths globally and an EU cost of 139 billion euros. Up to 40% of all deaths occur among the elderly. Despite all medical efforts, the 5-year mortality was reduced significantly less than that of malignant diseases. This highlights the urgent need to overcome the difficulties associated with present pharmacological therapies (i.e. drug instability, and unspecific targeting) by developing new ground-breaking therapeutic strategies that go far beyond any current regimens. New approaches for safe, efficient, and heart-specific delivery of therapeutics are strongly required.
To know more
read the Cupido Press Release
CUPIDO
is envisioned to meet these critical needs by providing an unconventional and effective strategy based on nanoparticle-assisted delivery of clinically available and novel therapeutics to the diseased heart. CUPIDO will develop innovative bioinspired hybrid nanoparticles formulated as biologicals delivery, which are i) biocompatible and biodegradable, ii) designed for crossing biological barriers, and iii) guidable to the heart. A combination of multidisciplinary manufacturing and validation approaches will be employed, bringing the envisioned product beyond the currently available clinical and day-to-day management of CD individuals. Scale-up production and respect of medical regulatory requirements will allow CUPIDO to deliver a final product for future late pre-clinical and clinical studies. Altogether, CUPIDO will foster the translation of nanomedical applications toward the cardiac field, which although still in its start, offers great potential to overcome the limitations associated with the currently pharmacological treatments.
The project involves 12 partners from Italy, Germany, Norway, UK, Greece, France and Luxembourg, of which 8 Industrial partners, both Large Enterprises and SMEs, including CITC Ltd, 2 Universities and 2 Research organisations, coordinated by the Italian National Research Council.
Read More
Press release
- Funding from innovateUK on Resilient Electronic Patch
“Re-Patch”
Cambridge, 19 September 2017
-
CITC Ltd and Zinergy UK to collaborate on CITC’s Patch4Life™ platform
.
Working with another innovative Cambridge-based start-up company, CITC Ltd secures funding to further develop its wireless wearable platform Patch4Life™ towards the thinnest, lightest and smartest personal monitoring bio-electronic smart patch device.
CITC’s medical patch, Patch4Life™, which uses sensors to measure various health and environmental parameters and has the capacity to communicate wirelessly with the wearer will now include Zinergy’s ultra-thin battery and super capacitor technology in a new and exciting project called “Re-Patch”. This project will bring about a light, thin and flexible personal well-being monitor that will adapt it’s shape to the body thereby allowing for a more comfortable fit for everyday life.
Commenting about the project, Luigi Occhipinti, CEO, Founder and Director of Engineering at CITC Ltd says “We are trilled to work with Zinergy in a joint effort that will make Patch4Life(TM) a really unique smart patch device platform with unprecedented performance and comfort, suitable for 24/7 monitoring of personal health status” and adds “We believe that the success of this project will help position the two companies at the forefront of the booming wearable electronics market while providing the users with a safe "wear and forget” smart patch technology that improves their quality of life and personal safety."
Pritesh Hiralal, CEO of Zinergy UK, adds “This is a synergistic opportunity to showcase and ideal application in which thin electronics and thin batteries come together for improved usability an comfort. We hope this will set the scene for much further development in the field.
The project started in May 2017 and the feasibility phase, funded by innovate UK under the “Emerging and Enabling Technology - Round 1” call, will continue for 12 months, at end of which the new Patch4Life™ platform, powered by Zinergy technology, will be presented to the public.
Follow us on:


or click
here
to be taken to our webpage.
To know more:
- about Patch4Life™ click
here
- about Zinergy: “Zinergy UK Ltd is a start-up founded in 2015 with headquarters in Cambridge. Zinergy is emerging as a company developing state of the art, thin film printed batteries which are mechanically flexible, both primary and rechargeable.”
- about CITC Ltd: “CITC Ltd (Cambridge Innovation Technologies Consulting Ltd) is an SME based in Cambridge (UK) with the mission to provide innovation in high tech fields that require multi-disciplinary approaches and know-how: from bio-electronics, integrated smart sensors and systems to advanced medical solutions.”
Read More
Press release
- New insights into exosome signalling that may lead to advanced treatments for cancer
Cambridge,
3rd July 2017
-
Cambridge University scientists partner with CITC Ltd to advance a novel therapeutic enzyme from the bench to the bedside.
A team of scientists based at the University of Cambridge have discovered new insights into cellular signalling processes that may lead to advanced treatments for cancers types that depend on specific metabolic pathways to survive. Targeting those pathways has great potential for developing better and more selective drugs.
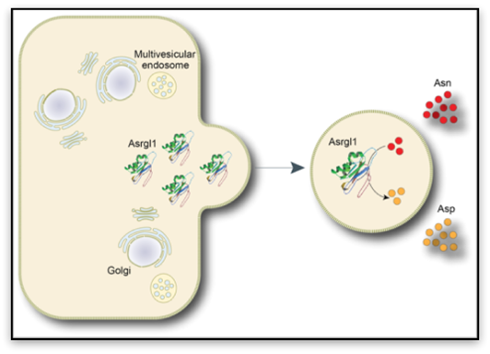
Stefano Pluchino from the Wellcome Trust – Medical Research Council (MRC) Cambridge Stem Cell Institute and Christian Frezza from the MRC Cancer Unit, used neural stem cells to study the extracellular vesicles (exosomes) that these cells release to communicate with the surrounding microenvironment.
By isolating stem cell exosomes, the scientists were able to measure their enzymatic activity and to discover that the most active enzyme was Asparaginase-like 1 ( Asrgl -1), an isoform of the enzyme L-asparaginase that is currently used to treat acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), a blood cancer often diagnosed in children and young adults. This discovery significantly extends our understanding of cell signalling biology and highlights potential clinical applications.
L-Asparaginase therapy for cancers such as ALL works by depleting Asparagine, an amino acid that cancer cells need to survive. However, the approved drug also depletes another amino acid, Glutamine, which healthy cells need to function normally while producing Glutamate that is toxic to the liver. Many patients also develop hypersensitivity to the bacteria-derived L-Asparaginases currently used in the clinic.
Critically, the team of scientists at Cambridge found that the Asrgl -1 isolated in exosomes acts specifically on Asparagine, while leaving Glutamine untouched.
The team lead by Pluchino will look to advance this work from the bench to the bedside with the help of Cambridge Innovation Technologies Consulting Limited (CITC Ltd), a Cambridge (UK) based biotechnology firm with vast expertise in drug development and neural stem cell based-therapeutics.
“The current treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia presents a difficult balancing act: removing enough asparagine so that cancer cells cannot survive, but leaving enough glutamine to ensure normal cells in the body can thrive”
, explains Pluchino, University Reader in Regenerative Neuroimmunology at Cambridge University and Chief Scientific Officer (CSO) at CITC Ltd. “The discovery that the Asparaginase-like 1 in stem cell exosomes depletes Asparagine but does not affect Glutamine could provide an alternative anti-cancer therapy that may limit side effects that can occur when Glutamine is transformed into Glutamate”.
Read the full article here
Read More
Press release
- Directly induced neural stem cells (iNSCs) for personalised stem cell therapies of neurological diseases
Cambridge, 21 February 2017
- CITC Ltd has recently concluded a non-esclusive license agreement with Provendis GmbH, a technology transfer agency of 27 universities of North Rhine-Westphalia, including the University of Bonn, for a manufacturing technology of autologous induced neural stem cells (iNSC) from adult cells that are harvested from simple skin biopsy or from other somatic sources.
Directly reprogrammed autologous iNSCs are seen as a powerful and safe tool to treat patients with neurological illnesses and injuries, that may occur while they age.
In line with CITC ltd’s governing mission, this license agreement helps develop further our unique portfolio of technologies and Intellectual Property in the field of molecular diagnostics, nano-medicine, and advanced therapies, and to establish a translational path toward clinical use in humans, subject to successful clinical trials.
Luigi Occhipinti, CITC Ltd’s Founder and Director of Engineering says
?The burden of neurological disorders in ageing population is projected to increase dramatically and we look forward to work with partners and investors to help bring innovative stem cell therapies available for clinical use at the earliest convenience”.
Prof. Frank Oliver Stefan Edenhofer, inventor, says:
“The induced neural stem cells (iNSC) technology carries tremendous potential for the study and cure of neurological disorders. After years of cumbersome basic research and successful patenting, now, we have to bring it from the lab bench to bed-side. Thus, we are happy to have with CITC a potent partner who will elaborate on the clinical realization of our induced neural stem cells (iNSC) technology”.
About CITC Ltd
CITC Ltd is a high-tech start-up based in Cambridge (UK) specialised in high-tech fields/high-growth sectors requiring multi-disciplinary approaches and know-how: from bio-electronics, smart sensors and systems to advanced solutions for nano-medicine, cell-therapies, and drug delivery.
CITC Ltd works with a strong team of scientists, engineers and medical experts to innovate within both the health care and medical fields and to improve people’s quality of life and costs of care.
www.citc-ltd.co.uk
About PROvendis GmbH
PROvendis is the technology transfer agency of 27 universities and offers for exclusive access to a broad and comprehensive technology portfolio for all kinds of technology-oriented companies. The agency aim is to transfer innovations and research materials that are protected by property rights from the universities to the industry and make them thus beneficial for the entire society.
www.provendis.info
Read the full story here
(German version)
or here
(English version)
Read More
|