humaNaseInvestigating the therapeutic potential of human Asparaginase-like protein 1 (hASRGL1)
Cancerous cells are notorious for undergoing metabolic changes and require amino acids such as L-asparagine (ASN) to grow. A powerful therapeutic strategy against some cancers, notably Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia (ALL), has been to starve the cells of ASN by utilizing the enzyme L-asparaginase (ASNase) which converts ASN to aspartate which cannot be used by cancerous cells. The ASNase enzymes currently employed clinically are derived from bacteria, meaning they frequently invoke allergic reactions in patients, and they can give rise to toxic side effects due to unwanted glutaminase (GLS) activity of the ASNase.
This project aims to investigate a potential remedy to these shortcomings by characterising the efficacy and therapeutic potential of the ASNase alternative human Asparaginase-like protein 1 (hASRGL1)

B2B aims at Modelling spontaneous Breast cancer metastasis to the Bone with a first-of-its-kind 3D device that recapitulates physiological tissue-level complexity.
The aim of the device would be to dissect the complexity of the metastatic process and empower high-throughput drug screening in a physiological context in order to gain a better understanding of this mechanism and potentially lead to the identification of metastasis-supressing therapies.
The B2B Consortium collects the excellence of several sectors, each one contributing to a specific component of the device.
 CUPIDO has been envisioned to provide an effective strategy for the treatment of Cardiovascular Disease based on nanoparticle-assisted delivery of clinically available and novel therapeutics to the diseased heart.
This project will develop innovative bio-inspired hybrid nanoparticles formulated as biological delivery, which are:
1. Biocompatible and biodegradable
2. Designed for crossing biological barriers
3. Guidable to the heart
A combination of a multidisciplinary approach to manufacturing and validation with 12 partners worldwide will foster the translation of nanomedical applications toward the cardiac filed, which offers great potential to overcome the limitations associated with the current pharmacological treatments.
Patch4Life ™ The World’s Lightest and Smartest “Wear-and-Forget” Companion Device for Ambient Assisted Living
This medical patch, Patch4Life TM uses:
- Sensors to measure various health and environmental parameters such as a potential fall, glucose levels and context related information such as light.
- Has the capacity to communicate wirelessly with the wearer and will now include Zinergy’s ultra thin-battery and super capacitor technology in a new and exciting project called “Re-Patch”.
This project will bring about a light, thin and flexible personal well-being monitor that will adapt its shape to the body thereby allowing for a more comfortable fit for everyday life.
Body gateway
- Physical activity monitoring
- Environmental parameters
- Chemical and biochemical from skin (patent pending)



Applications
-
Activity monitoring & Event detection (e.g. fall)
-
Chronic disease monitoring (e.g. glucose)
-
Context-related information (T,RH,Light)
-
Dual mode operation: indoor (subGHz harvester, illuminated + rech. battery) and outdoor (2.4 GHz radio Bluetooth Low Energy)
To know more about
Patch4Life
™ please contact
us.
iStem4Life
™
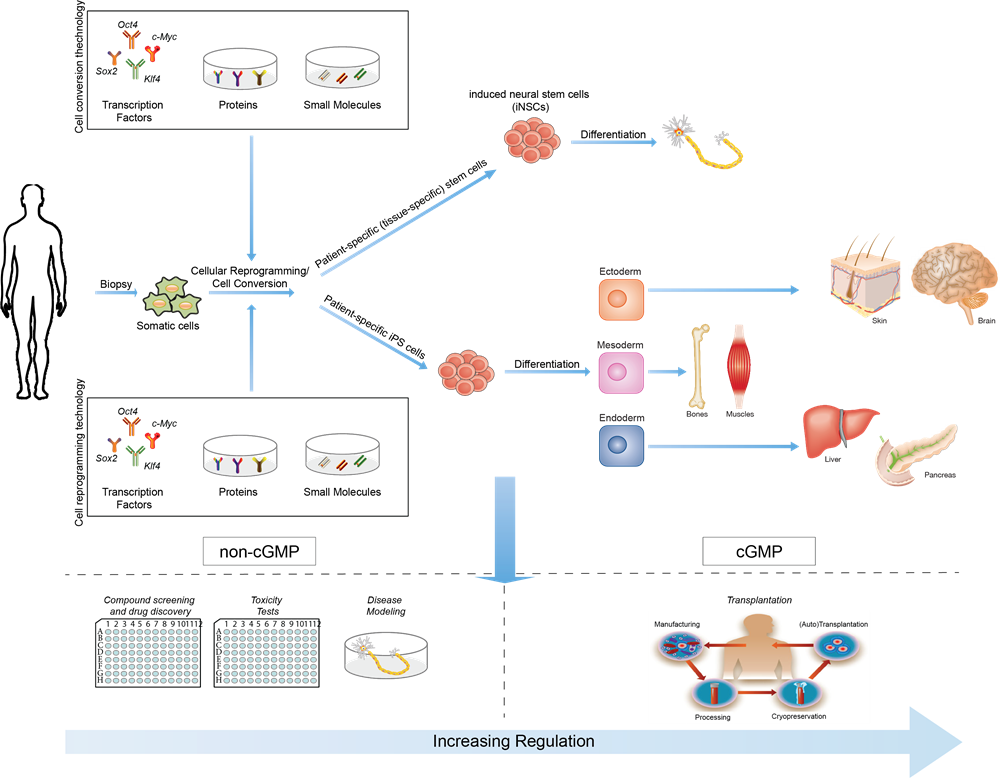
Harvesting, reprogramming and storage of autologous stem cells for treatment of neurological disorders
In complex neurological diseases, such as multiple sclerosis, stroke or spinal cord injuries, a treatment with stem cells may be the sole remaining choice of cure: stem cells can replace damaged cells or profoundly mitigate host immune responses – even in the central nervous system. Successful clinical studies are yet not existing since researchers are facing several hurdles in stem cell therapies, such as the use of embryonic stem cells that are ethically problematic; adult stem cells that are difficult to collect or hard to be expanded in a therapeutically sufficient amount.
A gleam of hope was provided by an invention to convert adult cells of the body into so-called induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells by genetic engineering, which opened new perspectives for stem cell therapy: those cells resemble naturally occurring stem cells, and they can subsequently be differentiated into various tissues, e.g. blood, liver, or nervous cells. Shinya Yamanaka and John Gurdon have been awarded the Nobel Prize for physiology and medicine in 2012 for this option of an ethically unproblematic generation of stem cells. The therapeutic breakthrough held off thus far since this technique has the risk of aberrant development and uncontrolled proliferation of the induced pluripotent stem cells.
Thanks to CITC Ltd’s recently licensed technology from University of Bonn, it is now possible to use a modified version of the Nobel Prize-awardees technique, in a way that brain stem cells equivalent to those present in the central nervous system, so-called induced Neural Stem Cells (iNSCs), are generated through a new cellular reprogramming, with no use of embryonic cells, high efficiency (therefore producing sufficient amounts for therapeutic use) and, most importantly, in a safe and non-toxic manner with no risk of aberrant development and uncontrolled proliferation as for iPS.
iStem4Life™
aims at accelerating the translational path from lab to hospitals while looking at opportunities to develop partnership programs and investment plans that help bring innovative stem cell therapies available for clinical use upon validation through clinical trials.
iStem4Life™
’s roadmap and IP portfolio encompasses all stages from the result of fundamental research, standard operating procedures for adult stem cell collection from skin biopsy or other somatic sources, bio-engineering methods and good manufacturing practice (GMP)-based cellular reprogramming of adult stem cells, e.g. fibroblasts, into safely expanded iNSCs, and storage in bio-banks, for use in clinical trials, first, and transplantation in humans, upon approval for therapeutic use.
See recent press releases from
CITC Ltd
and
Provendis GmbH
B
io-
E
lectronic
N
euro-phrostetic
D
evices for
A
ctive regeneration post CNS injuries (BENDA)
To know more about
BENDA
, please
contact us
|